How do hair transplants work? Hair loss is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide, especially with male pattern baldness. Whether due to genetics, medical conditions, or aging, the loss of hair can significantly impact one’s self-esteem and confidence. Thankfully, modern medical advancements have introduced effective solutions, with hair transplants being one of the most popular options. This article will delve into the science behind hair transplants, the different techniques available, the procedure itself, potential risks and benefits, and post-operative care.

Understanding Hair Loss
Before exploring hair transplant procedures, it’s essential to understand why hair loss occurs. Hair loss, or alopecia, can result from various factors, including:
- Genetics: The most common form is androgenetic alopecia, also known as male or female pattern baldness. It’s primarily driven by genetics and hormones.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like alopecia areata, thyroid problems, and scalp infections can lead to hair loss.
- Medications: Certain drugs used for cancer, arthritis, depression, and heart problems may contribute to hair thinning.
- Stress and Lifestyle: High-stress levels, poor diet, and lack of sleep can also impact hair health.
- Age: As people age, hair growth slows, and hair follicles shrink, resulting in thinning hair.
Understanding the root cause of hair loss is crucial for determining the most effective treatment.
What Are Hair Transplants?
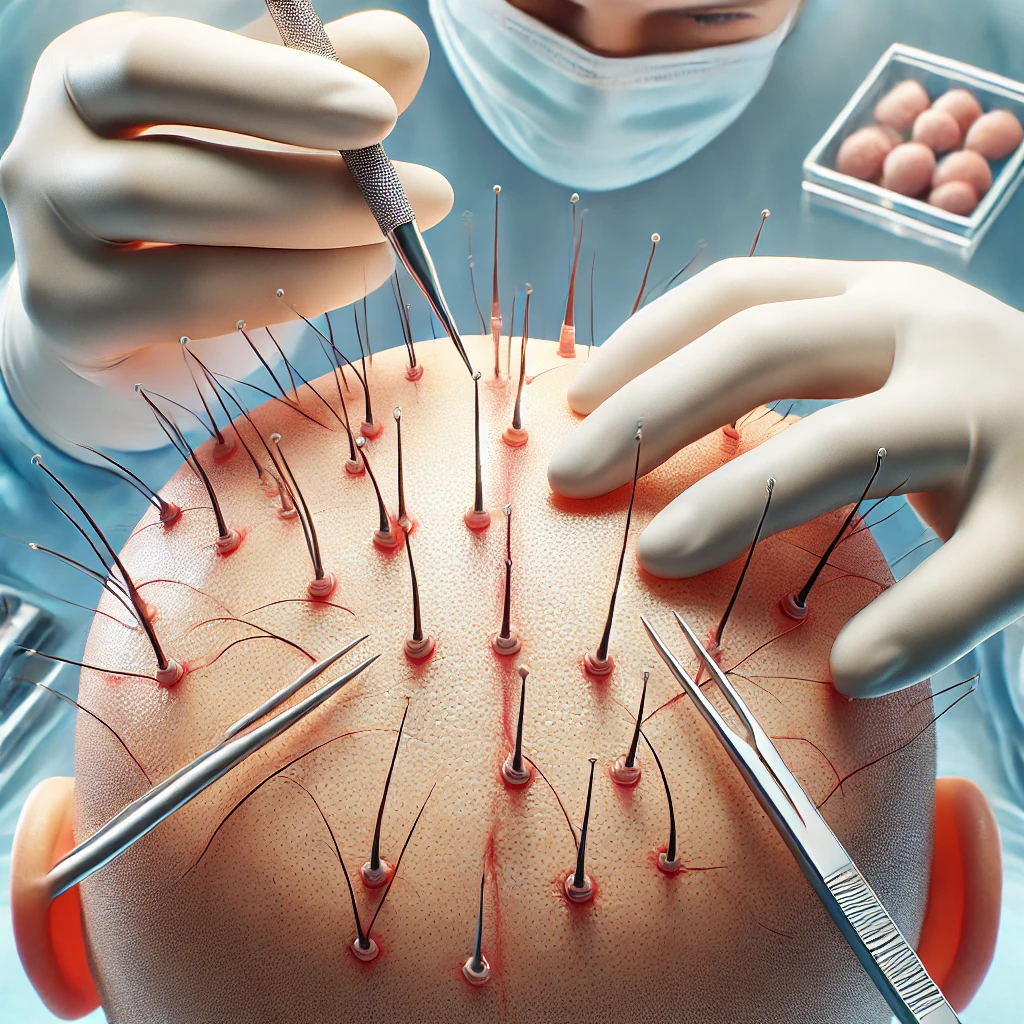
Hair transplants are surgical procedures that involve moving hair follicles from one part of the body, typically the back or sides of the scalp (the donor area), to a bald or thinning area (the recipient area). This method effectively treats various types of baldness, offering a permanent solution by utilizing the patient’s natural hair.
History of Hair Transplants
Hair transplantation has evolved significantly since its inception. The first documented case of hair restoration surgery was in the early 19th century when Dr. Okuda, a Japanese dermatologist, developed a technique for restoring hair by implanting small sections of skin containing hair follicles. However, it wasn’t until the 1950s that modern hair transplant techniques began to take shape, thanks to the pioneering work of Dr. Norman Orentreich, who demonstrated that transplanted hair retained its characteristics, a concept known as “donor dominance.”
Techniques of Hair Transplantation
There are two primary techniques used in hair transplantation today: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Each method has its unique process, advantages, and drawbacks.
1. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), also known as the “strip method,” involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, usually at the back of the head. This strip is then dissected into individual follicular units containing one to four hair follicles. These units are meticulously implanted into the recipient area.
Procedure:
- Anesthesia: The patient receives local anesthesia to numb the donor and recipient areas.
- Strip Removal: A surgeon removes a strip of scalp from the donor area.
- Dissection: The strip is dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope.
- Incision: Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area to implant the grafts.
- Graft Insertion: The follicular units are placed into the incisions, considering the natural hair growth pattern.
- Suturing: The donor area is sutured, leaving a linear scar that will be covered by surrounding hair.
Advantages of FUT:
- Higher Yield: FUT can yield more grafts in a single session, making it suitable for extensive baldness.
- Preservation of Follicles: The method ensures minimal damage to the follicles during extraction.
- Cost-Effective: Generally, FUT is more affordable than FUE due to the higher number of grafts obtained.
Disadvantages of FUT:
- Scarring: FUT leaves a linear scar, which may be visible if the patient wears their hair short.
- Longer Recovery: The recovery time can be longer compared to FUE.
- Invasiveness: The procedure is more invasive, requiring sutures and resulting in a tighter feeling in the scalp initially.
2. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a minimally invasive technique that involves extracting individual hair follicles from the donor area using a specialized punch tool. These follicles are then implanted into the recipient area.
Procedure:
- Anesthesia: The patient receives local anesthesia to numb the donor and recipient areas.
- Extraction: Individual follicles are extracted using a micro-punch tool, leaving tiny circular scars.
- Incision: Small incisions are made in the recipient area for implantation.
- Graft Placement: The extracted follicles are carefully placed into the incisions, mimicking natural hair growth.
Advantages of FUE:
- No Linear Scar: FUE leaves tiny scars that are nearly invisible and heal quickly.
- Shorter Recovery: The recovery period is generally shorter than FUT.
- Flexibility: Suitable for patients who prefer shorter hairstyles or have tight scalps.
Disadvantages of FUE:
- Time-Consuming: The process is more time-consuming due to the individual extraction of follicles.
- Higher Cost: FUE can be more expensive due to the complexity and time required.
- Limited Grafts: FUE may not be suitable for extensive baldness, as it yields fewer grafts per session.
Choosing the Right Technique for Hair Transplant
The choice between FUT and FUE depends on various factors, including the patient’s hair loss pattern, the number of grafts needed, the patient’s preference for scarring, and budget considerations. Consulting with a qualified hair transplant specialist is crucial to determining the most suitable method for each individual.
The Hair Transplant Procedure
Regardless of the technique chosen, the hair transplant procedure involves several key stages. Here’s a step-by-step overview:
1. Consultation and Planning
The journey begins with a thorough consultation with a hair transplant surgeon. During this stage, the surgeon evaluates the patient’s hair loss pattern, assesses the donor area’s density, and discusses the patient’s expectations and desired outcomes. A personalized treatment plan is then developed, outlining the number of grafts required and the best technique for achieving optimal results.
2. Pre-Operative Preparation
Before the surgery, patients may be advised to:
- Avoid Blood Thinners: Medications like aspirin should be avoided to minimize bleeding during the procedure.
- Refrain from Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and alcohol can hinder the healing process and should be avoided before surgery.
- Wash Hair: Patients should wash their hair thoroughly to ensure a clean scalp for the procedure.
3. Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is administered to the donor and recipient areas to ensure the patient’s comfort throughout the surgery. In some cases, mild sedation may also be provided to help the patient relax.
4. Extraction
Depending on the chosen technique (FUT or FUE), the extraction process begins. In FUT, a strip of scalp is removed and dissected, while in FUE, individual follicles are extracted using a punch tool. The surgeon takes great care to preserve the integrity of the follicles during this process.
5. Graft Preparation
The extracted follicles or strip is carefully prepared for transplantation. Technicians separate and clean the grafts, ensuring they are healthy and ready for implantation.
6. Incision and Implantation
Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area, considering the natural hair growth pattern to achieve a natural-looking result. The prepared grafts are then meticulously inserted into these incisions.
7. Post-Operative Care
Once the procedure is complete, the patient receives instructions for post-operative care, which may include:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications may be recommended to manage any discomfort.
- Antibiotics: To prevent infection, patients may be prescribed antibiotics.
- Avoiding Physical Activity: Patients should avoid strenuous activities for a few days to prevent graft displacement.
- Gentle Hair Care: Special care instructions for washing and handling hair are provided.
Hair Transplant Recovery and Results
The recovery period after a hair transplant varies depending on the technique used and the individual patient. Here are some key points regarding recovery and expected results:
1. Initial Healing
- Swelling and Redness: Mild swelling and redness in the treated area are common but typically subside within a few days.
- Scabbing: Small scabs may form around the grafts, which naturally fall off within a week or two.
- Itching: Some itching is normal but should be avoided to prevent dislodging grafts.
2. Hair Shedding
It’s essential to understand that transplanted hair will initially shed within the first few weeks. This shedding is a natural part of the process and should not cause concern, as it makes way for new hair growth.
3. Hair Growth
New hair growth typically begins around three to four months after the procedure. Patients can expect noticeable improvement within six to nine months, with full results visible after 12 to 18 months. The transplanted hair will continue to grow naturally, blending seamlessly with the existing hair.
Risks and Potential Complications of Hair Transplants
As with any surgical procedure, hair transplants come with potential risks and complications. However, these are generally rare and can be minimized by choosing an experienced and qualified surgeon. Some possible risks include:
- Infection: Though uncommon, infections can occur if post-operative care instructions are not followed.
- Scarring: While FUT leaves a linear scar, FUE results in tiny scars that are usually less noticeable.
- Shock Loss: Temporary hair thinning in the donor area can occur but is typically reversible.
- Unnatural Appearance: Poorly executed transplants can result in an unnatural appearance, highlighting the importance of selecting a skilled surgeon.
Benefits of Hair Transplants
Despite potential risks, hair transplants offer numerous benefits, making them a popular choice for individuals seeking to restore their hair:
- Natural Results: Transplanted hair looks and grows naturally, as it uses the patient’s follicles.
- Permanent Solution: Unlike topical treatments or wigs, hair transplants provide a permanent solution to hair loss.
- Boost in Confidence: Restoring hair can significantly enhance self-esteem and confidence, positively impacting one’s overall quality of life.
- Minimal Maintenance: Transplanted hair requires no special maintenance beyond regular hair care routines.
Alternative Hair Restoration Options
While hair transplants are highly effective, they may not suit everyone. Alternative hair restoration options include:
1. Medications
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): An over-the-counter topical solution that stimulates hair growth.
- Finasteride (Propecia): A prescription medication that inhibits hormone-related hair loss.
2. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)
LLLT devices, such as laser combs and helmets, use low-level lasers to stimulate hair follicles and promote growth.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves injecting the patient’s platelet-rich plasma into the scalp to stimulate hair growth and improve hair density.
4. Scalp Micropigmentation
This non-surgical procedure involves tattooing tiny pigments onto the scalp to create the illusion of hair follicles and add density to thinning areas.
Conclusion
Hair transplants have revolutionized the field of hair restoration, offering individuals a permanent and natural solution to hair loss. With advancements in techniques like FUT and FUE, patients can achieve remarkable results tailored to their needs and preferences. However, selecting a skilled and experienced surgeon is crucial to minimize risks and achieve the best possible outcome. Whether opting for a hair transplant or exploring alternative treatments, individuals experiencing hair loss can find hope in modern solutions that restore hair and confidence, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.

